Dans tout ce chapitre, nous considérerons a un réel non nul.
I. Résolution de l’équation du second degré :
1. Définition et vocabulaire :
- Une équation du second degré, à une inconnue x, est une équation qui peut s’écrire sous la forme
, où
sont trois réels donnés avec
.
- Résoudre l’équation
, c’est trouver tous les nombres
tels que
.
- Un tel nombre p est dit solution ou encore racine de l’équation.
2. Résolution de l’équation du second degré :
Posons f(x) = ax²+bx+c avec .
2.1. Ecriture de f(x) sous forme canonique :
Puisque ,
ou
donc .
Cette dernière écriture est appelée forme canonique de f.
2.2. Résolution de l’équation ax²+bx+c=0 :
On pose ainsi
Premier cas :
Si alors
.
Le nombre entre crochets est strictement positif donc l’équation f(x)=0 n’a pas de solution.
Second cas :
Si alors
.
Puisque , l’équation f(x)=0 a une solution et une seule :
.
Troisième cas :
Si alors
et :
Si l’on pose :
et
alors
.
Donc puisque , l’équation f(x)=0 a deux solutions distinctes
et
.
Le nombre est appelé discriminant de l’équation du second degré
ou du trinôme
.
On le note ( lire « delta »).
a. Lorsque , l’équation n’a pas de solution dans
.
b. Lorsque , l’équation a une racine double :
.
c. Lorsque , l’équation a deux solutions :
et
.
II. Factorisation et signe du trinôme :
1. Factorisation du trinôme :
Nous avons vu, au cours de la démonstration du théorème 1 que si
alors
.
Lorsque l’équation f(x)=ax²+bx+c=0 a deux solutions et
( dans le cas
) alors,
2. Signe du trinôme :
- Lorsque
,
est toujours du signe de a.
- Lorsque
,
est du signe de a
- Lorsque
,
est du signe de a, sauf lorsque x est entre les racines, auquel cas f(x) et a sont de signes contraires.
Application :
Pour résoudre une inéquation du second degré, on détermine le signe du trinôme associé.
III. Représentations graphiques des fonctions trinômes :
La courbe de la fonction est une parabole. Cette parabole est tournée vers le haut lorsque
et tournée vers le bas lorsque
.
Synthèse :
Exemples :
Résoudre
Solution :
puisque
, le trinôme n’a pas de racine dans
.
De plus a=1 donc a>0 ainsi pour tout
réel et
.
Résoudre l’inéquation du second degré .
Nous avons .
L’équation a deux racines qui son t:
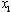
.
Nous avons donc
ainsi l’ensemble solution de l’inéquation du second degré
est l’intervalle
.
Télécharger et imprimer ce document en PDF gratuitement :
Vous avez la possibilité de télécharger puis d'imprimer gratuitement ce document «equations et inéquations du second degré : cours de maths en 1ère en PDF.» au format PDF.
D'autres cours et exercices à consulter
- Les suites numériques : cours de maths en 1ère en PDF.
- Position relative de deux droites dans l’espace : cours de maths en 1ère en PDF.
- La fonction exponentielle : cours de maths en 1ère en PDF.
- Dérivée d’une fonction : cours de maths en 1ère en PDF.
- Les suites numériques : cours de maths en 1ère en PDF.
- Probabilités : cours de maths en 1ère en PDF.
- Limites et asymptotes : cours de maths en 1ère en PDF.
- Le produit scalaire dans le plan : cours de maths en 1ère en PDF.







